CAR-T Tumor Immune Service
Cell therapy technology is on the eve of a major revolutionary breakthrough in science and technology, providing new hope for the treatment of some difficult human diseases. Governments, technology communities, businesses, and the public around the world are also highly concerned about the development of the cell industry, and its broad application prospects are becoming a new hope for safeguarding human health in the future. Cell immunotherapy represented by CAR-T is currently mainly applicable to children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non Hodgkin lymphoma, and has been considered one of the successful methods in the field of cancer treatment in recent years. CAR-T therapy mainly focuses on studying tumor associated antigens as targets, and exploring effective tumor targets is also a top priority of CAR-T therapy.
Service Number
|
Service Type
|
Specification
|
Price
|
Delivery Time
|
WZ160001
|
CAR-T plasmid construction;
CAR-T lentivirus packaging;
Lentivirus infection of T cells;
CAR expression efficiency detection;
Pharmacodynamic evaluation (validation of in vitro killing experiments);
|
/
|
inquiry
|
inquiry
|
一、Background introduction
1. Introduction to CAR-T
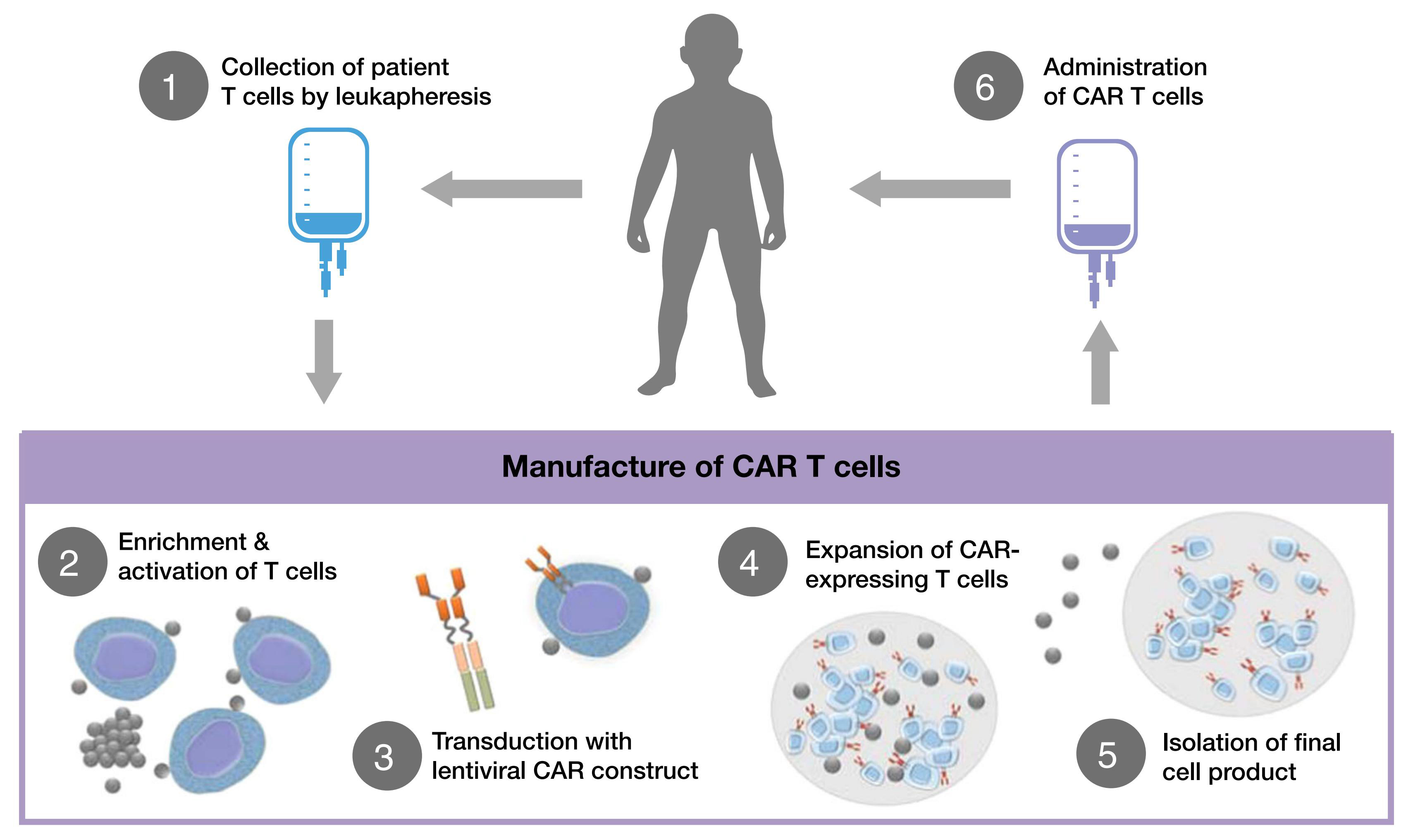
CAR-T, The full name is Chimeric AntigenReceptor T-cell Immunotherapy, which is a chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy. This cell therapy is a treatment method that uses genetic engineering technology to artificially modify T cells from tumor patients, which are cultured in large quantities in vitro to generate tumor specific CAR-T cells, and then reintroduced into the patient's body to attack cancer cells.
CAR-T treatment flowchart
(George Hucks1 and Susan R. Rheingold, Blood Cancer J. 2019 )
2. CAR structure
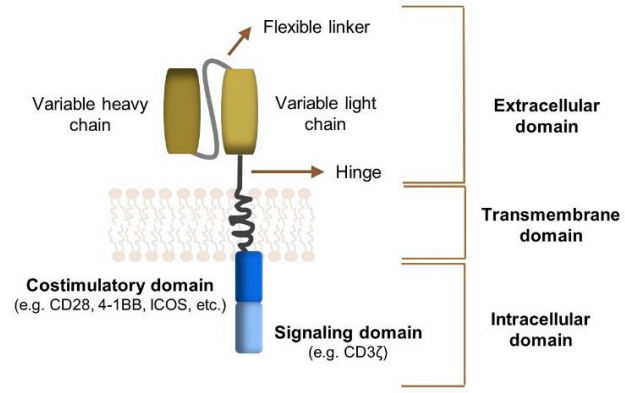
CAR consists of three main structural domains: extracellular antigen binding domain, transmembrane domain, and intracellular signaling domain.
The extracellular antigen binding domain consists of a single chain variable fragment scFv of a monoclonal antibody that recognizes and binds to the antigen, and a hinge region hinge that acts as a connecting element; The transmembrane domain can promote the expression of CAR on the surface of T cells; The intracellular signaling domain consists of a signal transduction structural domain and a co stimulatory domain (the first generation CAR has no co stimulatory domain), which is crucial for T cell activation.
Among them, the single chain variable fragment scFv is crucial as an antigen binding domain. It is connected to the intracellular signal domain through a transmembrane domain, recognizes and binds to antigens presented by cancer cells, and then transduces the extracellular antigen binding signal to CAR-T cells, activating downstream signal cascades.
CAR Structure Diagram
(T Abreu et al. Journal of Controlled Release. 2019 )
3. Development history of CAR carriers
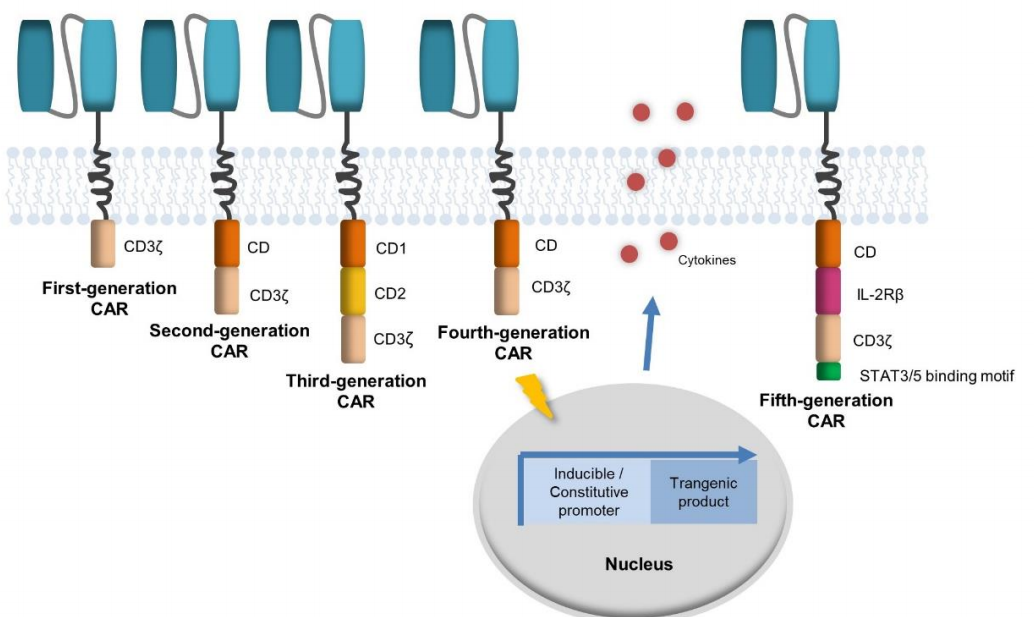
Up to now, CAR-T cell immunotherapy has been developed to the fifth generation. The first generation CAR only had one activation domain CD3 Zeta and no intracellular co stimulatory signals; The second and third generation CARs have been improved in the intracellular signaling domain, with 1-2 new intracellular signaling domains CD28 and/or 4-1BB (CD137) added each; The fourth generation CAR also introduced pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-12, IL-15, etc; The fifth generation CAR, on the basis of the second generation, adds co stimulatory domains that activate other signaling pathways, including IL-2R β and STAT3/5 binding motif domains, providing antigen dependent cytokine signaling.
The Development of CAR Carriers
(T Abreu et al. Journal of Controlled Release. 2019 )
The reason for the continuous improvement of CAR carriers: Although the first generation of CARs can locate tumor cells through antigen binding regions and activate T cells through CD3 Zeta in the signal domain, due to the lack of co stimulatory signals, it cannot guarantee the continuous expansion of T cells, resulting in weak anti-tumor effects and insufficient ability to eliminate tumor cells on a large scale. Therefore, the development of the second and third generation CARs mainly focuses on co stimulatory molecules. Researchers have added co stimulatory domains to make them survive longer in vivo, enhance their proliferation ability, and improve their ability to eliminate tumor cells. The fourth generation CAR overcomes the inhibition of tumor immune microenvironment by modifying the tumor microenvironment to recruit and activate other immune cells for immune response, further enhancing its killing effect on tumors; The fifth generation CAR can simultaneously trigger activation domain, co stimulatory domain, and cytokine signals, and has been shown to significantly enhance T cell proliferation, survival, and anti-tumor activity in both hematological and solid tumor models.
Due to the relatively mature second-generation technology, including two CAR-T drugs already on the market (Novartis' KYMRIAH and Gilead's YESCARTA) and currently under development products, most of them use second-generation CAR-T technology.
4. CART target selection
The tumor antigens of CAR-T mainly include two categories: tumor specific antigens and tumor associated antigens. Tumor specific antigens are only expressed in tumor cells, making them an ideal target for CAR-T therapy. However, the expression level of this antigen on the tumor surface is very low, which limits the application of CAR-T therapy. Therefore, current CAR-T therapy mainly focuses on tumor associated antigens as targets for research. These tumor associated antigens are highly expressed in tumor cells and lowly expressed in normal cells, such as CD19, CD20, CD30, which are widely studied targets.
CD19 is a normal and malignant B lymphocyte specific surface protein that plays an important role in the development, proliferation, differentiation, and malignant transformation of B cells. Due to its specificity in B lymphocyte expression and wide expression in malignant tumors of the B lymphatic system, CD19 has become an ideal target for CAR-T therapy of B cell tumors. At present, the CAR-T drugs approved for market by the FDA are all targeting CD19 and are all aimed at hematological malignancies, namely Novartis' KYMRIAH and Gilead's YESCARTA.
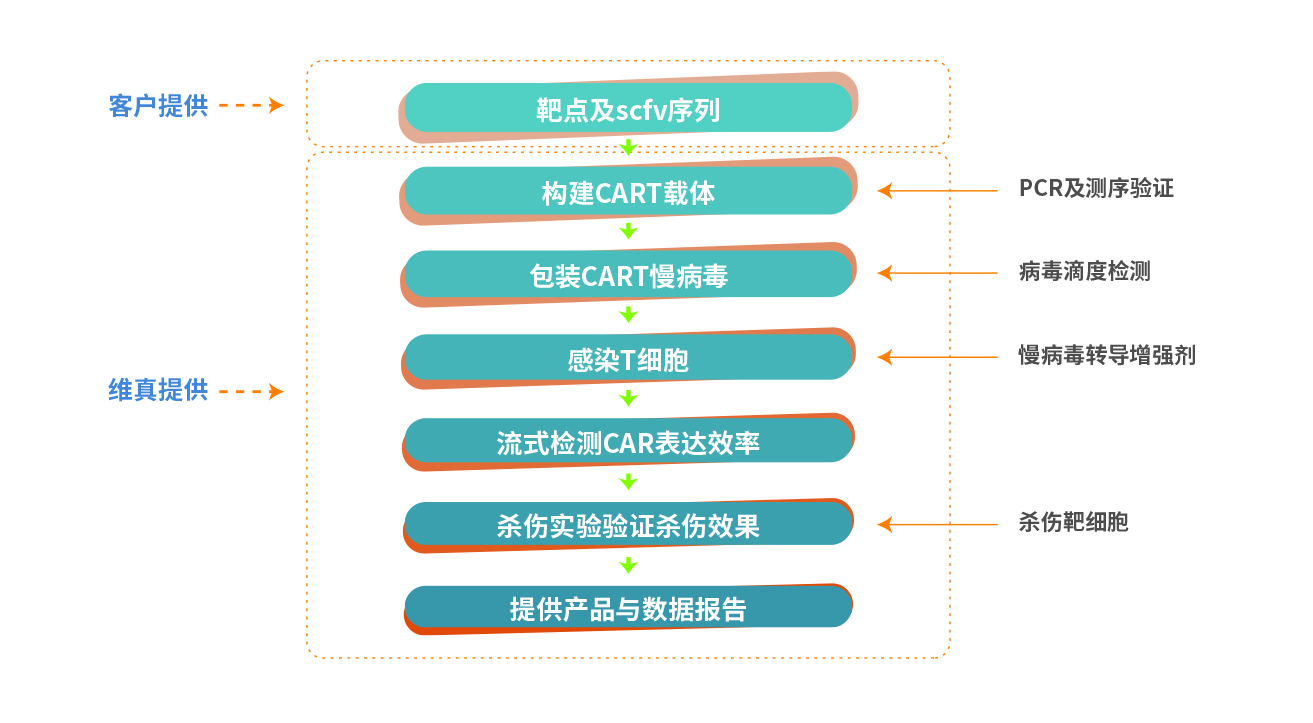
二、Service Content
Weizhen Biotechnology is committed to the construction and modification of preclinical gene expression vectors for gene and cell therapy. Currently, we have developed and launched a series of CAR-T products, including CD19 CAR-T vector/lentivirus, LVTE, a lentivirus transduction enhancer specially developed for suspension cells, and K562-CD19-GFP, a target cell for killing experiments. In addition to the above products, Weizhen can also provide CART tumor immune services for customers. As long as you provide the corresponding target and scfv sequence, we can construct CAR-T vectors, lentiviruses, and killing target cells targeting the target for you, and help you complete the in vitro validation of CAR-T cell killing function. We can do what you want and need. Step by step, make your gene/cell therapy preclinical research faster and smoother!