Site-directed mutagenesis is used to introduce specific mutation into the target DNA of known sequence. Depending on the base change, site-directed mutagenesis usually includes three types: base substitution, base deletion, and base insertion. According to whether the amino acid changes after the base changes, gene mutations can also be divided into three types: same sense mutations, missense mutations and nonsense mutations.
In basic research, researchers usually create a mutant gene through changing the DNA sequence to investigate the relationship between gene structure and its function; or generate a mutant protein by changing amnio acid sequence to study the relationship of between protein structure and its function. In this way, under physiological conditions, researchers can clarify the regulation mechanism of gene, the etiology and pathogenesis of disease from the micro level.
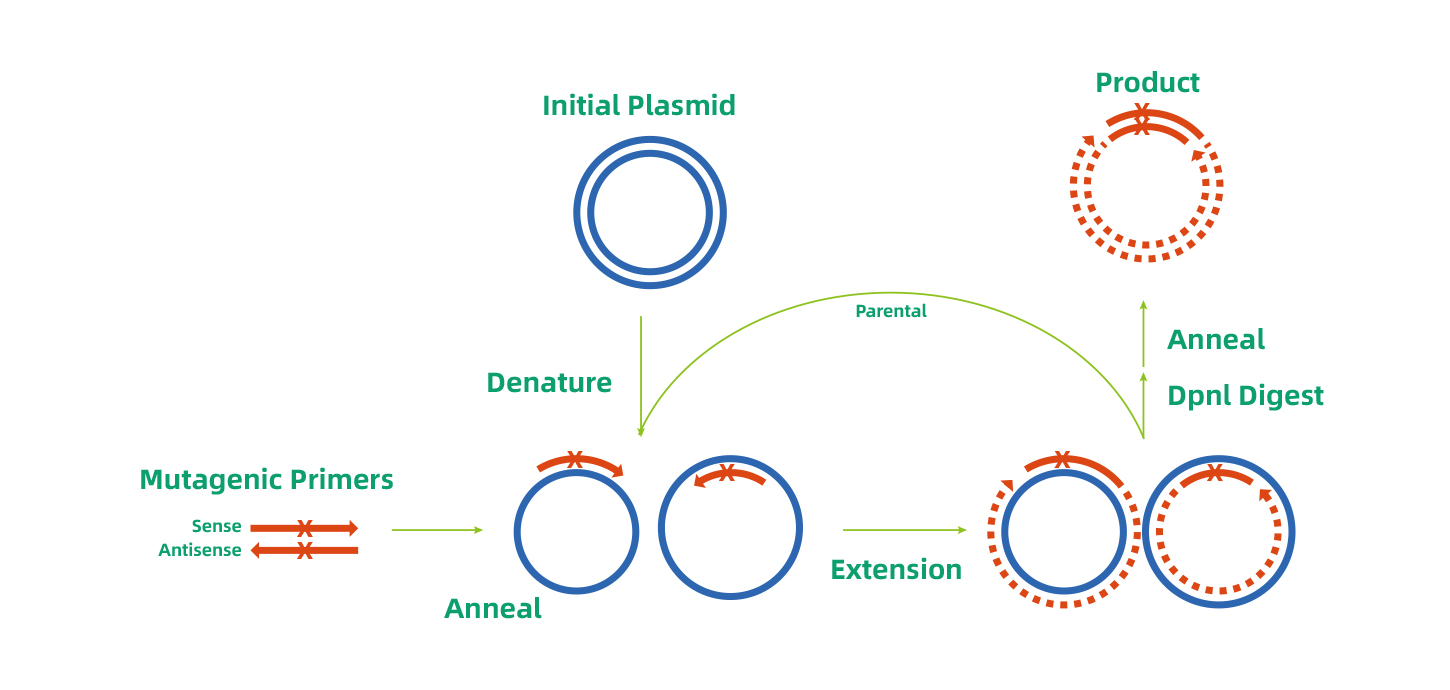
A most commonly used method for site-directed mutagenesis: PCR
The flow chart of performing site-directed mutagenesis by PCR: 1. Design mutagenic primers; 2. overlap PCR; 3. Template DNA is eliminated by a methylation-dependent endonuclease (i.e. DpnI); 4. The PCR product that are digested by DpnI are transformed into bacteria; 5. Positive clones selecting and sequencing. The flow chart is below:
|
1.
|
Ready-to-Use mutation templates: WZ Biosciences has two extensive human gene collection, including human ORF collection and human miRNA collection.
|
|
2.
|
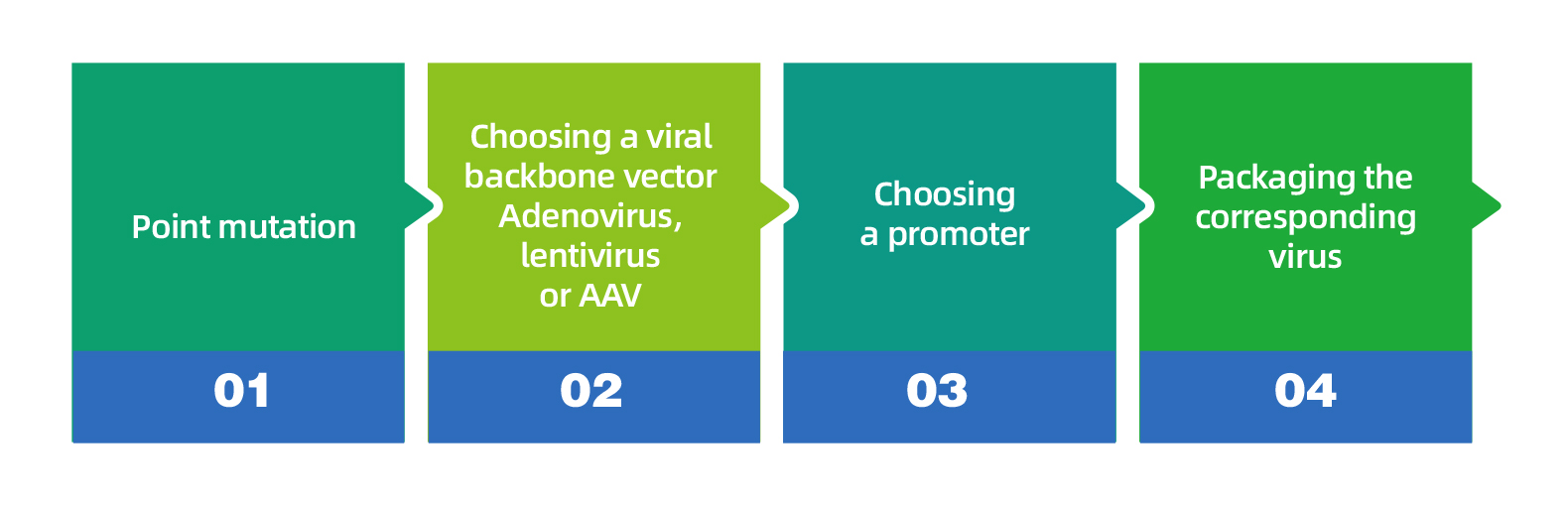
Intimate Follow-Up Services: WZ Biosciences can provide you with a variety of follow-up services such as subcloning, adenovirus packaging, lentivirus packaging, AAV packaging services and gene expression analysis.
|
|
3.
|
Fair and reasonable price.
|

|
《Transfection Reagent Instructions》
|
|
1. What materials and information do I need to provide for site-directed mutagenesis?
The materials to be provided by you:
If you will send your own vector for mutating or cloning, please send us at least 5 ug DNA or glycerol stock;
The information to be provided by you:
①Gene Name, sequence(pre-mutation sequence) and sequencing results;
②Description of sites/base pairs to mutate;
③Name of desired viral vector backbone or name of customer-provided vector.
2. How do you define one mutation?
One mutation is defined as any base changes within 6bp.
3. If I need to change the destination vector while mutating, how do you charge?
If you need to change the destination vector while mutating, additional cloning cost will be required.
|
1.
|
Aging (Albany NY). (IF=4.831). Li, et al. (2019). Sirt1-inducible deacetylation of p21 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation.
|
|