Dual luciferase reporter gene testing service
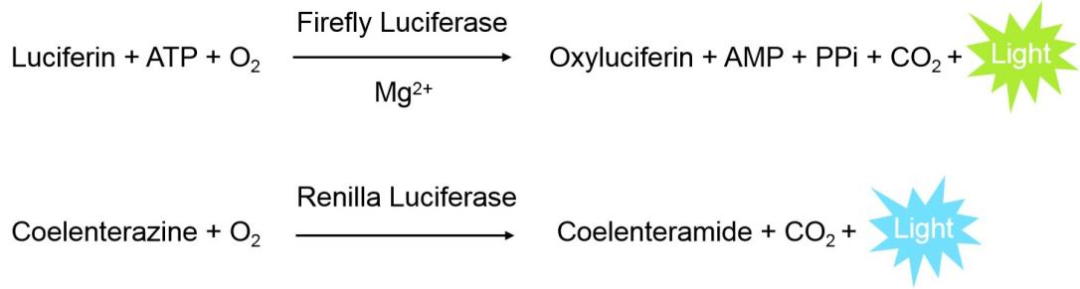
Luciferase is a general term for enzymes in nature that can produce bioluminescence. It can catalyze the oxidation of luciferin to oxidized luciferin and emit bioluminescence during the oxidation process. Luciferase has become an ideal reporter gene due to its excellent sensitivity, ease of use, and quantitative detection. There are many types of luciferase, among which firefly luciferase (FLUC) and Renilla luciferase (RLUC) are widely used.
Principle of dual luciferase catalyzed luminescence
Firefly luciferase is a 61kD monomeric enzyme that does not require post expression modification to obtain enzymatic activity. Its catalytic luminescence reaction requires the participation of ATP and luciferin. In the presence of ATP, Mg2+, and O2, luciferin is oxidized by luciferase to produce yellow green light with a wavelength of 540-600nm.
Sea kidney luciferase is a 36kD monomeric enzyme that does not require post expression modification to produce enzymatic activity. It only requires O2 to catalyze the oxidation of coelicin and emit blue light at a wavelength of 460-540nm.
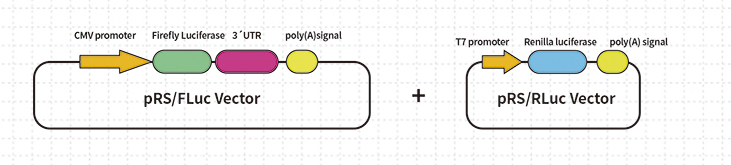
Dual luciferase reporter gene system
Due to the different catalytic substrates and luminescent colors of firefly luciferase and sea kidney luciferase, as well as their different light absorption wavelengths, they can be detected without interfering with each other. In addition, both enzymes have no endogenous expression in mammals, making them widely used as dual luciferase reporter gene systems. In dual luciferase detection, firefly luciferase is usually used as the experimental reporter gene, while sea kidney luciferase is used as the control reporter gene to reduce the influence of external factors such as cell activity and transfection efficiency on experimental accuracy.
1. Testing method
Co transfect the firefly luciferase reporter gene plasmid with the plasmid containing the Renilla luciferase gene into cells, or construct both reporter genes onto the same vector and initiate their expression using different promoters. Analyze the expression level of firefly luciferase by calculating the ratio of firefly luciferase detection value to Renilla luciferase detection value (Firefly Luciferase/Renilla Luciferase).
2. Application scenarios
The dual luciferase reporter gene system has become an important tool for studying gene transcription regulation, promoter structure analysis, promoter SNP analysis, and non coding RNA targeted interactions, thanks to its high sensitivity, wide detection range, and convenience and speed.
★ Weizhen Biological Dual luciferase Detection Service ★
Service Content 1: Service content one: Detection of interaction between promoters and transcription factors
Insert the target promoter fragment upstream of the firefly luciferase expression sequence, construct an experimental reporter gene plasmid, and co transfect the transcription factor expression plasmid to be detected with two reporter gene plasmids into relevant cells; After cell culture, the cells were lysed and the supernatant was collected by centrifugation. Then, two types of luciferase substrates were added, and luciferase reacted with the substrates to produce fluorescence. The activity of luciferase was measured by detecting the intensity of fluorescence to determine whether the transcription factor interacted with the promoter.
Note: If transcription factors can activate the target promoter, the firefly luciferase gene will be expressed, and the expression level of firefly luciferase is proportional to the strength of the transcription factor's action.
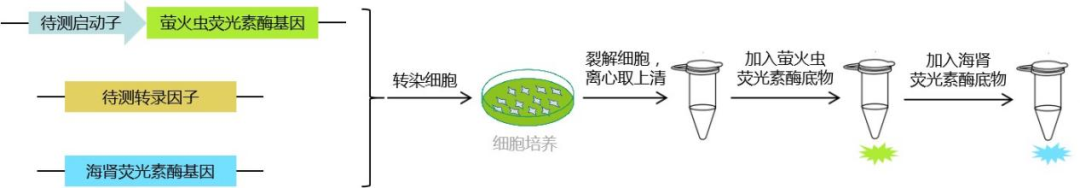
Schematic diagram of promoter transcription factor interaction detection
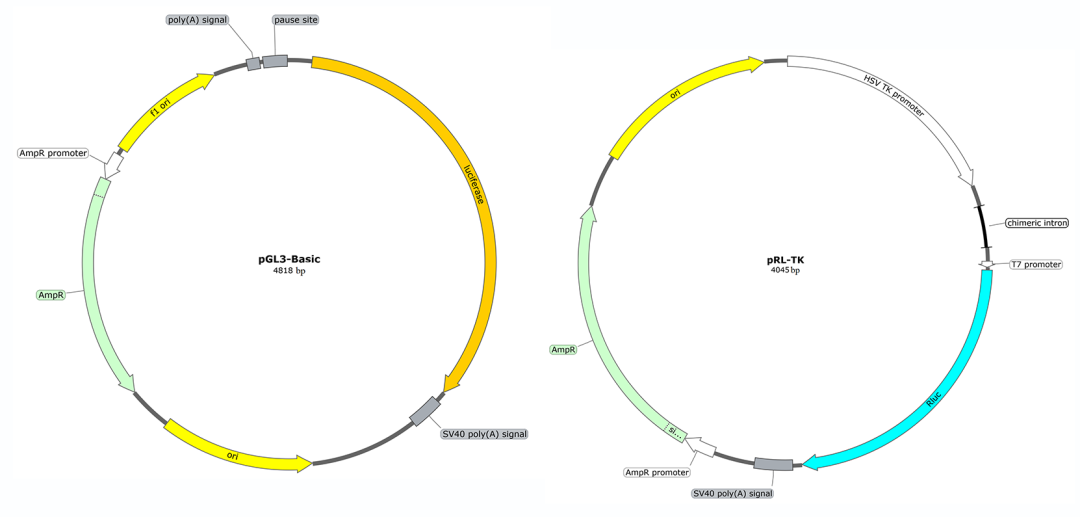
Related vectors:
Service Content 2: miRNA Target Gene Regulation Verification
MiRNA induces intracellular silencing complex mediated mRNA degradation or inhibition of mRNA translation by recognizing the 3'UTR region of mRNA. Construct the 3 'UTR sequence of the wild-type or mutant target gene to the 3' end of the firefly luciferase gene, co express the two reporter gene plasmids with miRNA in cells, and verify the regulatory effect of miRNA on the target gene by comparing the changes in the expression activity of firefly luciferase reporter genes.
Note: If the activity of luciferase decreases, it suggests that miRNA may be involved in inhibiting the expression of target genes.
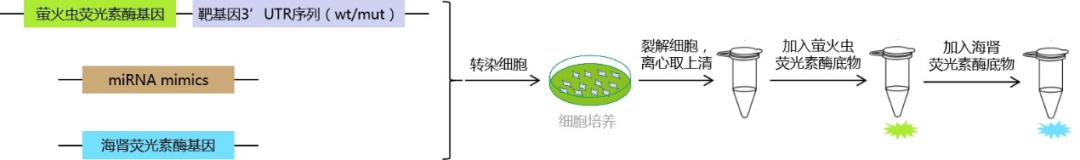
Schematic diagram of miRNA and target gene regulation validation
Related vectors:
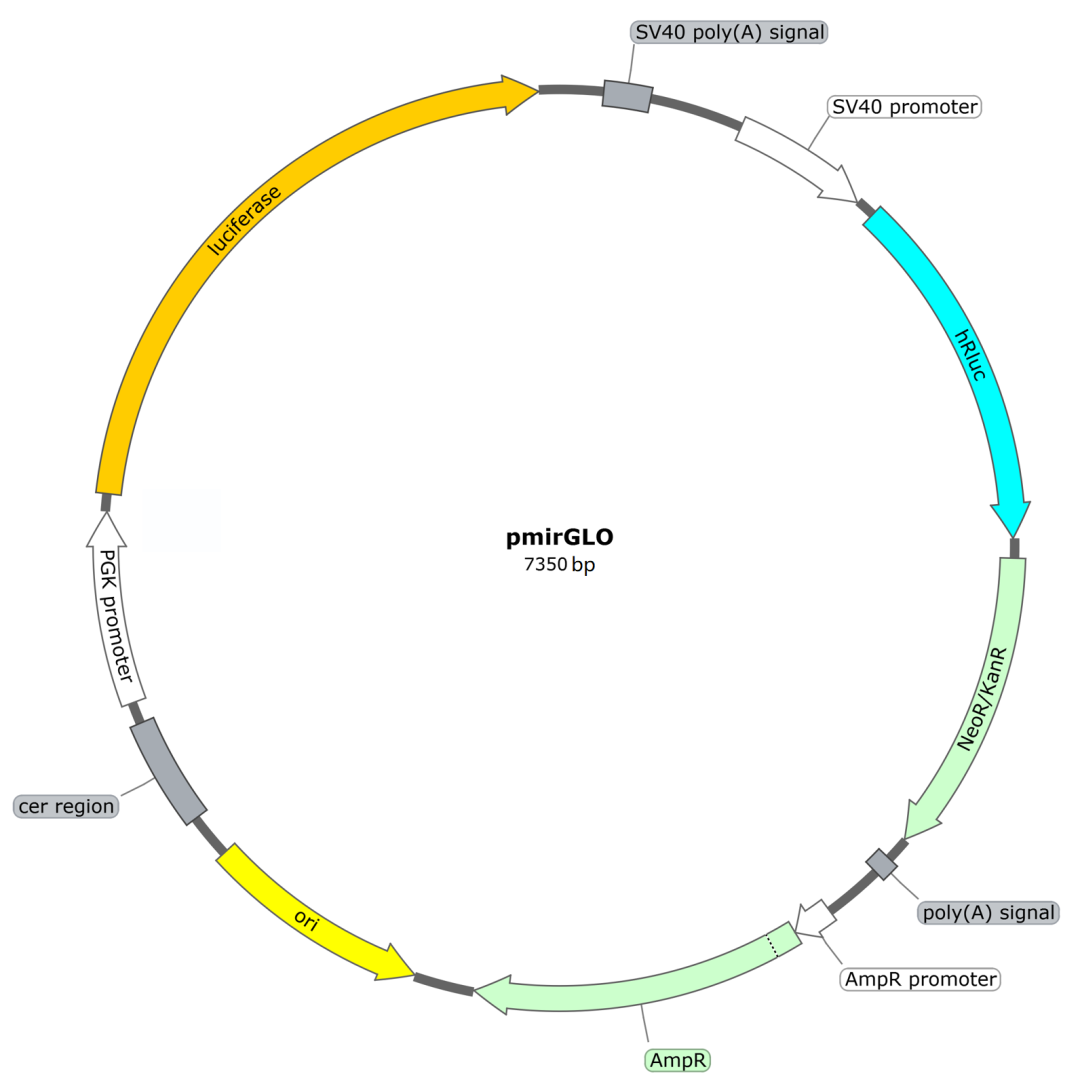
Service process:
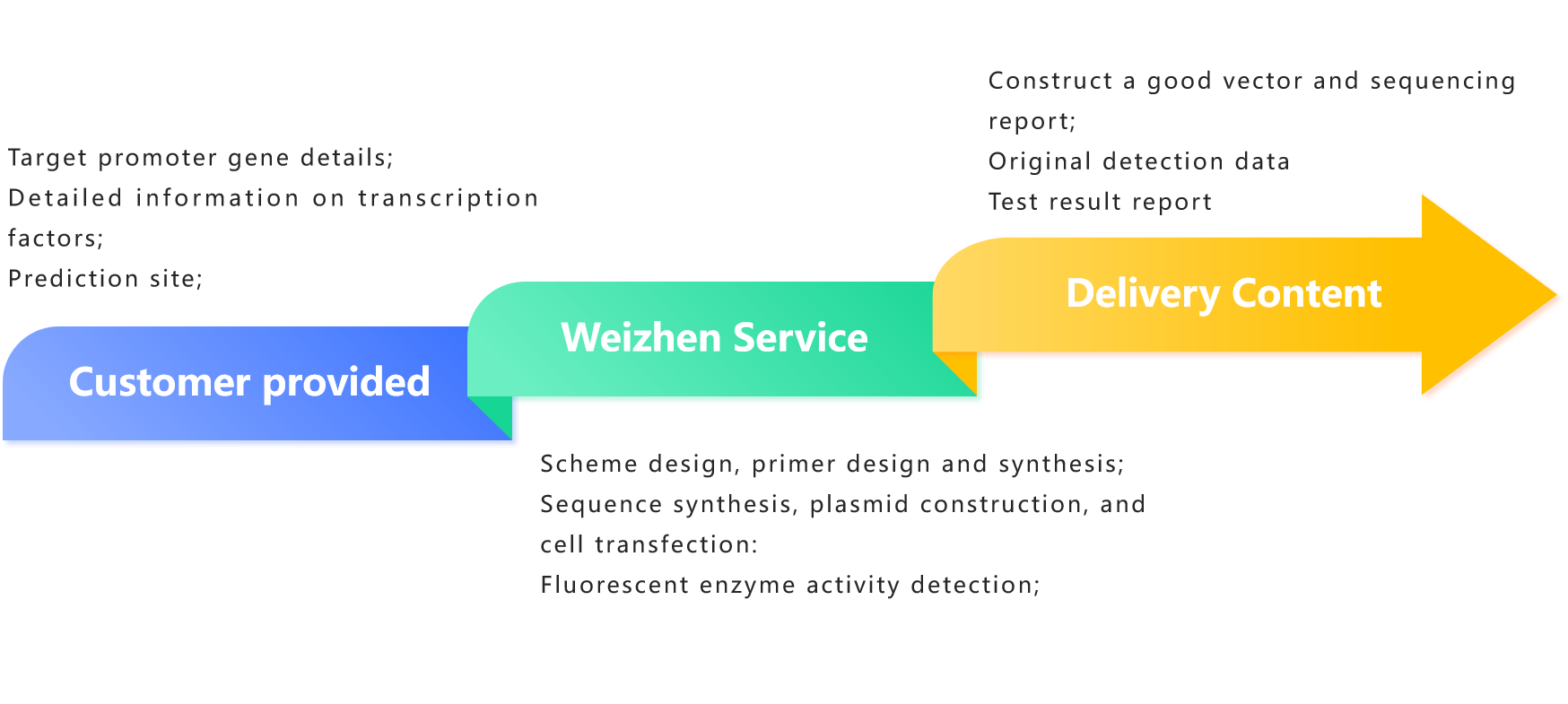
Detection of interaction between promoters and transcription factors
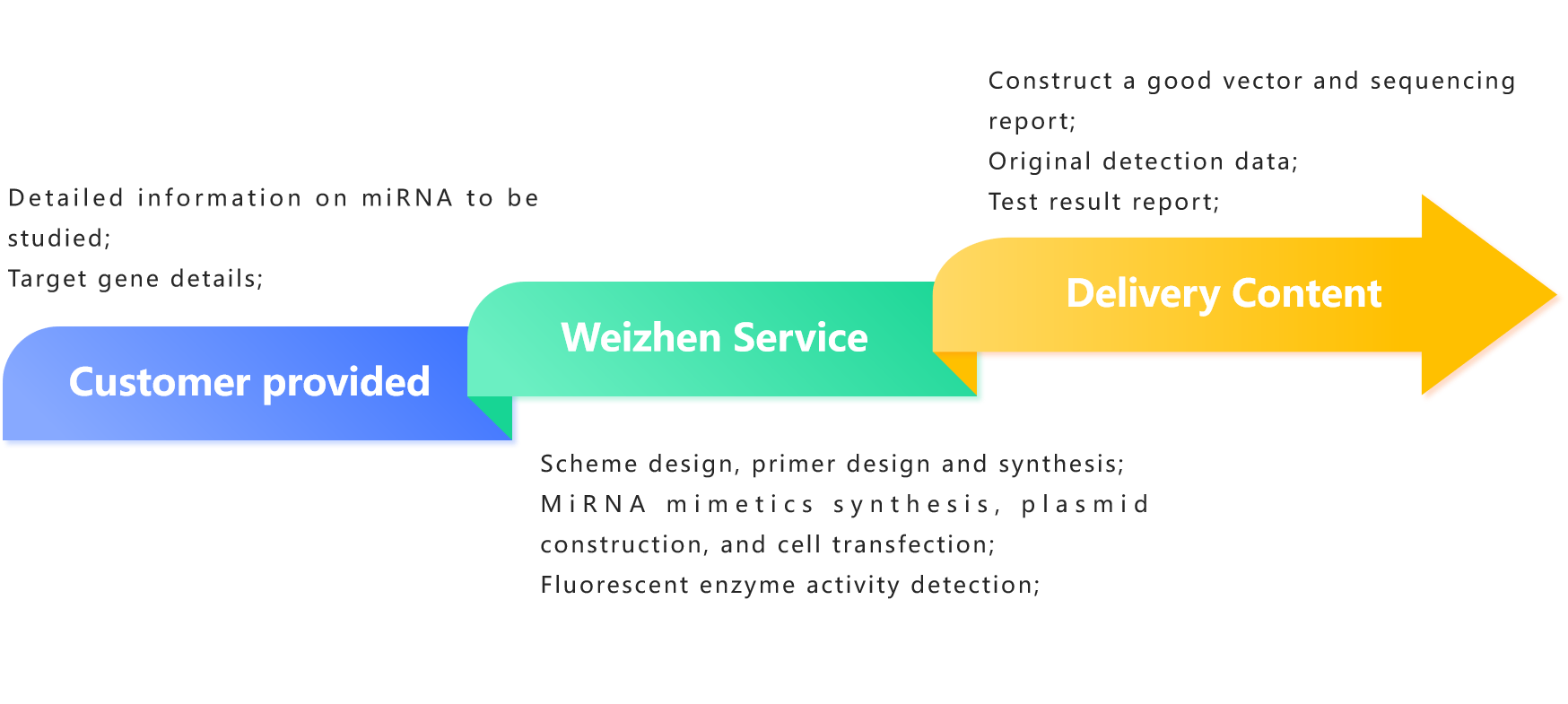
MiRNA and Target Gene Regulation Validation